Caching is a vital performance optimization technique that stores copies of files or data in a temporary storage location (the cache) for quick access. Implementing an effective caching strategy can significantly improve application speed, reduce load on servers, and provide a better user experience.
📦 What Is Caching?
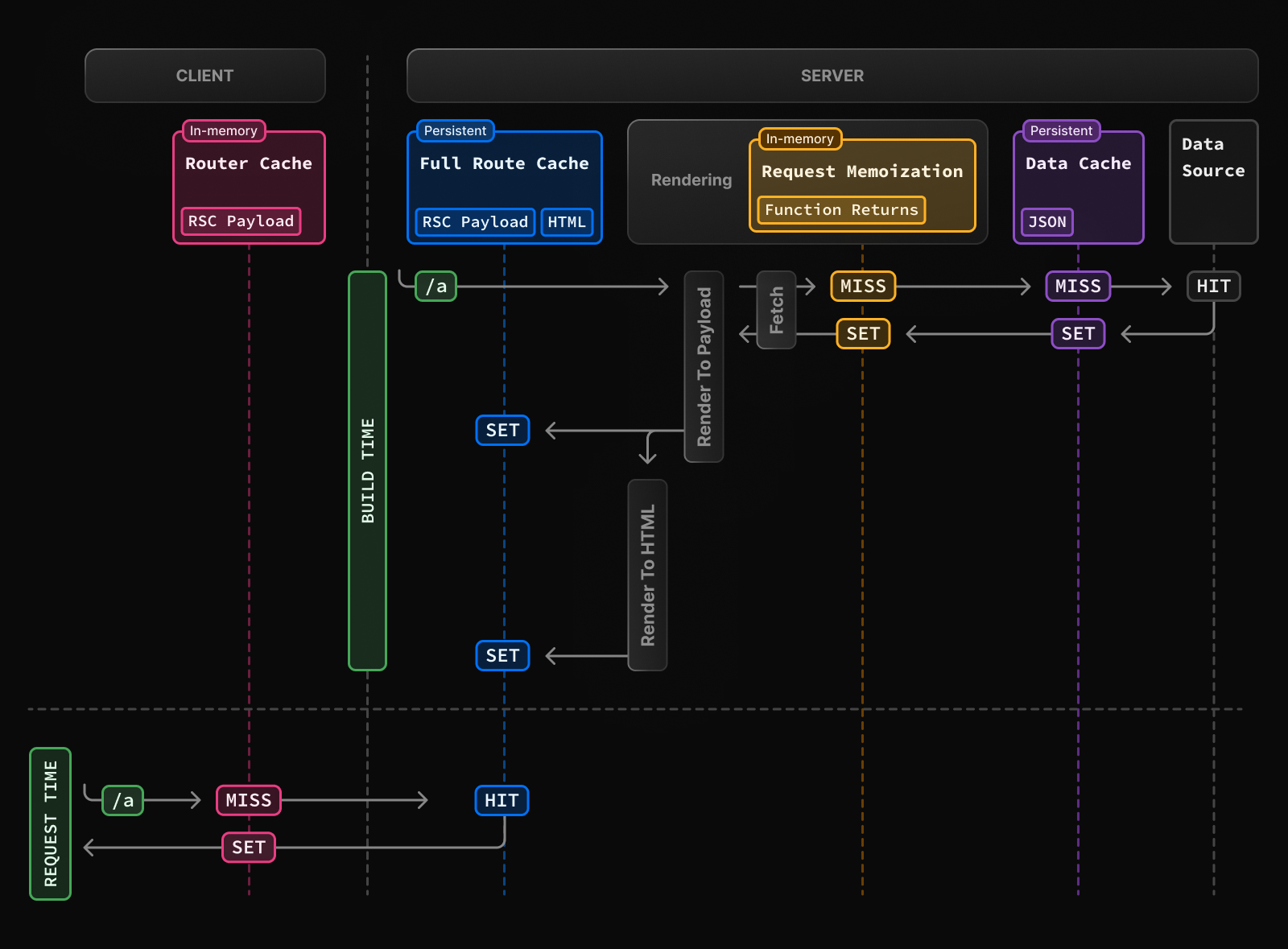
Caching temporarily stores data that is expensive to generate or retrieve. It reduces redundant work and improves performance.
🔍 Types of Caches
Here are a few common types of caches used in web development:
- Browser Cache: Stores static assets on the user's device.
- Server-side Cache: Used to cache rendered HTML or API responses.
- CDN Cache: Content Delivery Networks cache files geographically closer to users.
- Database Cache: Stores frequently accessed DB queries in memory (e.g., Redis).
- Application-level Cache: Caches computed data (e.g., with in-memory stores like LRU cache).
🛠️ Caching Strategies
| Strategy | Description | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Cache-Control | Sets caching policies via HTTP headers | Caching images or static assets |
| ETag / Last-Modified | Allows conditional requests based on content changes | API responses |
| Stale-While-Revalidate | Serve stale content while fetching updated content in the background | Next.js ISR |
| Manual Invalidation | Explicitly clear/update cache when data changes | Admin dashboard updates product list |
🧪 Example: Caching API Response in Node.js
const express = require("express");
const app = express();
const cache = new Map();
app.get("/api/data", async (req, res) => {
if (cache.has("data")) {
return res.json({ cached: true, data: cache.get("data") });
}
const data = await fetchFromDatabase();
cache.set("data", data);
setTimeout(() => cache.delete("data"), 1000 * 60); // Cache for 1 min
res.json({ cached: false, data });
});